Do you know the term 'Bushido'? Bushido refers to a unique set of morals and philosophies that developed throughout Japanese history and deeply influences modern Japanese culture. This concept encompasses the morals and behavioral ideals held by Japanese samurai, shaping their lifestyle, ethical views, and codes of conduct.
In this discussion, we will explore the essence of Bushido, its origins, how it developed over time, and its impact on our lives today.
The Origin of Bushido

The origins of the system of ethics and behavior held by the Japanese samurai, known as Bushido, can be traced back to the Heian period. During this era, samurai served as private warriors for the imperial family and the aristocracy, developing their own values and codes of conduct in the process. Bushido was influenced by Confucianism, Buddhism, and Shinto, emphasizing values such as loyalty, courage, honor, humility, courtesy, honesty, and patience.
During this time, samurai shaped their actions and thoughts according to these principles. For example, loyalty meant absolute allegiance to one's lord and was considered one of the most important virtues for a samurai. Courage referred not only to bravery on the battlefield but also to the mental strength to do what is right. Honor was closely tied to a samurai's social status, and failing to uphold Bushido was seen as the ultimate disgrace. Humility and courtesy formed the behavioral standards for samurai in daily life, serving as crucial elements in showing respect and reverence to all people. Honesty and patience were seen as indicators of a samurai's character, demonstrating perseverance and continuous effort even in difficult situations.
These principles impacted every aspect of a samurai's life, influencing their actions, decisions, and even daily behavior. Bushido transcended mere martial skills to become a cultural framework defining the samurai's identity and way of life. In this way, Bushido became the foundation of philosophy and lifestyle for the samurai class, deeply embedding itself as a concept in Japanese society and culture. It functioned not just as a set of ethical standards but as a spiritual guide for the samurai
The Catalyst for Bushido's International Recognition
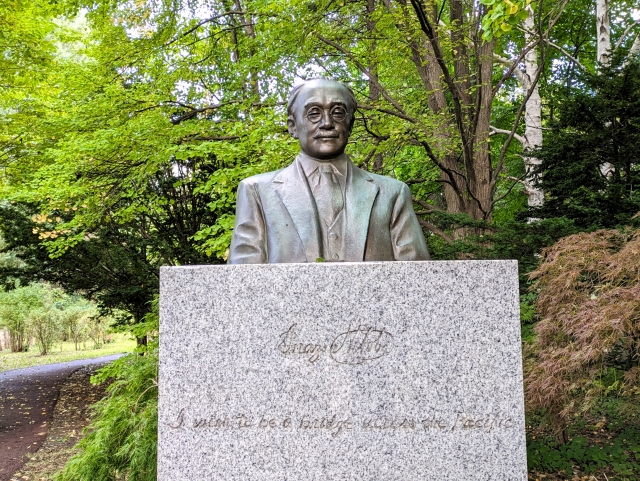

The world began to take notice of Japan with surprise and fascination following its victory in the war with China (1894-1895). During this period, Japan was undergoing rapid modernization and expanding its international influence. Under these situation, Nitobe Inazō's introduction of Bushido provided deep insights into Japanese culture to the world.
Nitobe Inazō introduced the values of Bushido, rooted in Japan's samurai class, to the world through his book 'Bushido: The Soul of Japan' in 1900. In 'Bushido', Nitobe portrayed the core values of loyalty, honor, courage, and sincerity not only as the essence of the samurai class but also as fundamental to the attitudes and national character of the Japanese people at large. He suggested that the Japanese ethical mindset was cultivated within the environment of being raised as the children of samurai, embodying 'Bushido' as the norm that underpins Japanese thought and action. Nitobe demonstrated how these values were intertwined with Japan's rapid modernization and helped Western readers gain a deeper understanding of Japanese culture.
Japan's international success during this era provided a significant boost to Nitobe Inazō's introduction of Bushido. The global recognition of Japanese Bushido was linked not only to its philosophical depth but also to the rising international stature of Japan. Nitobe's work played a crucial role in showcasing the uniqueness and universality of Japanese culture, serving as a catalyst in spreading Japan's spiritual heritage worldwide.

The Bushido embodied by the samurai continues to have a significant impact on modern Japanese people.
In the Japanese education system, the spirit of Bushido is incorporated into the moral education of students. For example, the strict teaching of manners in schools reflects the respect and humility of Bushido. Additionally, in group activities and club activities, the spirit of hierarchical relationships and teamwork is emphasized, reflecting the loyalty to a lord and sense of community found in Bushido.
In the Japanese business world, the values of Bushido underpin corporate culture. For instance, the core Bushido value of loyalty manifests as long-term commitment to a company, with many employees working for the same organization for many years, a practice not commonly found in Western societies. The sincerity and sense of responsibility from Bushido are reflected in companies' attitudes towards continuous effort until achieving the desired quality.
The influence of Bushido can also be seen in everyday life in Japan. For example, the attitude of valuing politeness and order in public places strongly reflects the influence of Bushido, making it a unique aspect of Japanese culture. Similarly, the culture of valuing an individual's honor and the reputation of the family is rooted in the Bushido concept of honor.
However, with the advancement of modernization and globalization, there is a tension between the traditional values of Bushido and the demands of contemporary society. For instance, the system of lifetime employment and excessive loyalty can impact individuals' career choices and work-life balance. This situation presents a challenge in seeking a balance between traditional and modern values.
Summary
How was it for you? Bushido was the system of ethics and behavioral ideals cherished by the samurai. Furthermore, Bushido has influenced the way modern Japanese people think. This spirit of Bushido is a unique mindset possessed only by the Japanese in the world. As Japanese living in the modern age, we have the responsibility to appreciate the value of Bushido and to pass it on to the next generation. We must live our daily lives with pride in being Japanese, and spare no effort in conveying the spirit of Bushido to future generations